Bluetooth versions

Definition of Bluetooth versions
Bluetooth is The primary difference between Bluetooth versions is that the most modern Bluetooth versions offer faster data transfer rates. Bluetooth offers greater connection range and reliability and provides better security than previous Bluetooth versions.
What is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard used to exchange data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and to create personal area networks (PANs). In the most commonly used mode, transmission power is limited to 2.5 mW, giving a very short range of up to 10 meters (33 ft). It employs UHF radio waves in the ISM band from 2.402 GHz to 2.48 GHz. It is mainly used as an alternative to wired connections to exchange files between nearby portable devices and to connect cell phones and music players to wireless headphones.
What is the definition of Bluetooth versions?
a computer network technology that is basically used to connect various electronic devices without using cables. It is specifically used to collect and transfer data, such as files, images, videos, sounds, etc.
The main purpose of Bluetooth is to facilitate the transmission of information between different types of devices through connection technology. Bluetooth technology relies on establishing connections over short distances, which are easily managed between closely related devices.
Bluetooth technology has different versions, such as Bluetooth 1.x, 2.x, 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, etc. Each version typically features improved connection speed and performance, allowing for new features and fine-tuning resources. New versions usually add new specializations as well as new device-related content.
Following are the required features of different Bluetooth versions.
Bluetooth has evolved over the past twenty years since version 1.0 debuted in 1999. The Bluetooth standard has adapted accordingly, with range and data throughput changing focus from version 1.0 to version 3.0 to version 4.0 to correct a course towards power efficiency with Bluetooth Low Energy. Let's take a look at how wireless communication protocols have evolved over the years.
Bluetooth 5.3 (2021)
Bluetooth 5.3 is an upgrade or version of the Bluetooth protocol for 2021. Notable new features of this version may include improved battery usage efficiency on mobile devices or increased data transfer speeds.This Bluetooth version incremental upgrade, version 5.3, adds more stability, security and efficiency.
Bluetooth 5.2 (2020)
This Bluetooth LE Power Control (LEPC) provides adjustable power Enhanced Feature Protocol (EATT) LE maintains parity between client and server.
Bluetooth 5.1 (2019)
More antennas provide greater tracking accuracy and faster pairing by retraining generic attribute (GATT) profile caching requirements.
Bluetooth 5 (2016)
A more powerful version with extended battery life, the BT 5 has extended the outdoor transmission range from 50 to 200 meters. Location services are improved because they can communicate more information before establishing a connection. The first smartphones to support BT 5 are the Galaxy S8 and the iPhone 8 and X.
Bluetooth 4.2 (2014)
BT 4.2 increases the payload size in Bluetooth packets by 10x, delivering 2.5 times more data. Supports the low-power wireless personal area network (WPAN) version of IPv6 (6LoWPAN).
Bluetooth 4.1 (2013)
More efficient data exchange and better connectivity with LTE frequencies. BT 4.1 enables Bluetooth devices to communicate with each other maintaining connectivity with less manual effort.
Bluetooth 4 (2010)
Introduced Low-Power Bluetooth Low Energy.
Bluetooth 3 + HS (2009)
Branded as Bluetooth 3.0 + HS (High Speed), it initiates the connection via Bluetooth but transmits data via Wi-Fi.
Bluetooth 2.1 (2007)
Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) has been added to make pairing faster and safer. Encryption is enforced, improving security and using less power.
Bluetooth 2 (2004)
Branded as Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate), the three-bit encoding (as opposed to one) increased the data rate from 1 to 3 Mbps (2.1 Mbps in practice).
Bluetooth 1.2 (2003)
BT 1.2 Bluetooth (Basic Data Rate) was the first widely used Bluetooth. Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH) helps avoid interference from Wi-Fi and other technologies on the same frequency. Pairing speed has been improved.
Bluetooth 1.1 (2001)
improving reliability and interoperability; most are backwards compatible but not 100%.
Bluetooth 1.0 and 1.0B (1999)
The first Bluetooth space. There were deployment problems that prevented BT from quickly gaining ground.
How does Bluetooth work?
Bluetooth is a communication protocol that transmits data and information between devices with specific ease. A Bluetooth device can communicate with other Bluetooth devices when they support the same Bluetooth profile. A convenient feature of Bluetooth communication is the ability to establish strong pairing between wireless devices.
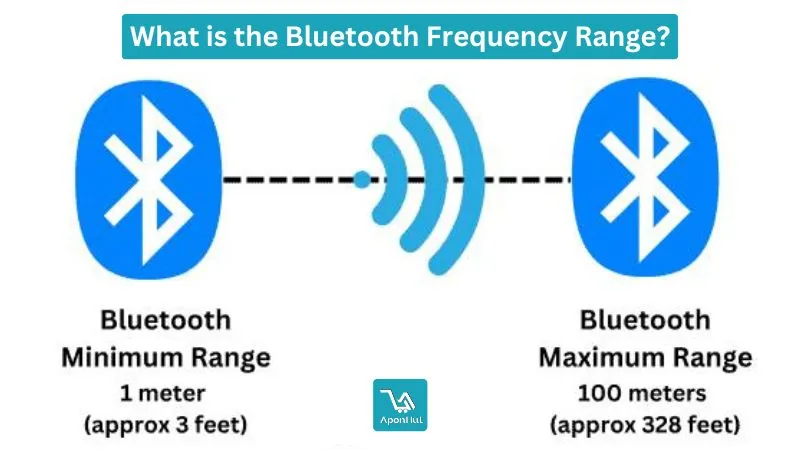
Bluetooth works similarly to Wi-Fi by converting data into radio frequency waves in the 2.4 GHz spectrum (read more about it here). But unlike Wi-Fi, which has a range of 50 meters indoors and twice as much outdoors, Bluetooth is more concerned with keeping transmission power low to preserve battery life and avoid radio interference with devices. It works on the principle of creating a network (PAN), otherwise known as a piconet. A Bluetooth device with a minimum range of 10 meters has a total transmission power rating below 2.5 mW. The simple ad hoc (peer-to-peer) nature of a Bluetooth connection also reduces electronic complexity and, therefore, implementation cost, making it suitable for connecting to inexpensive peripherals such as headsets and input devices.
While widely available Class 2 Bluetooth devices operate at ranges of 10 meters and beyond, Class 3 Bluetooth radios are limited to a maximum of a single meter for most wearable applications. While the Bluetooth specification mandates a range of 10 meters and above for Class 2 devices, Class 1 Bluetooth equipment used in industrial applications can be paired with high-powered radios to extend well beyond the 100-meter range.
Different versions of Bluetooth
Since the introduction of Bluetooth 1.0 in 1999, Bluetooth has undergone many changes. Although its original purpose was to replace wired serial communication, the method of transmission has evolved with each iteration of Bluetooth. This article will provide an overview of how Bluetooth has changed over the past 20 years.
Versions 1.0–3.0: Bluetooth Classic
When we talk about each iteration of Bluetooth, three factors help differentiate between the different versions: range, data speed, and power consumption. These factors are determined using modulation schemes and data packets. However, back then, Bluetooth 1.0 was much slower than what we have now. Data speed is limited to 1 Mbps, and the range reaches only 10 meters.
The Bluetooth version uses a modulation scheme called Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK). With GFSK, the modulated carrier is shifted between two frequencies, representing 1s and 0s.
When Bluetooth 2.0 came out, GFSK was superseded in favor of two new schemes: p/4-DQPSK and 8DPSK, which use waveform phase shifts to carry information as opposed to frequency modulation.These two schemes have data speeds of 2 Mbps and 3 Mbps respectively. Bluetooth 3.0 further improved data speeds by adding 802.11 for data transfer up to 24 Mbps, although this was not a mandatory part of the 3.0 specification.
Due to the high power requirements of Bluetooth versions 1.0–3.0, also known as Bluetooth Classic,
Version 4.0–5.0: Bluetooth Low Energy
To meet the growing demand for wireless connectivity between small devices, Bluetooth 4.0 was introduced to the market along with Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
The latest version of the Bluetooth protocol, Bluetooth 5. It's still geared toward low-powered applications, but it improves on BLE's data rate and range. Unlike version 4.0, Bluetooth 5 offers four different data rates to accommodate different transmission ranges: 2 Mbps, 1 Mbps, 500 kbps, and 125 kbps. Since the increase in transmission range required a reduction in data rate, the lower data rate of 125 kbps was added to support applications that benefit more from improved range. For example, small sensors are not needed to send large amounts of data, so reducing the data rate allows these sensors to transfer information up to 240 meters. Data transmission applications at 2 Mbps are developed where the range is expected to be short but can greatly benefit from the increased data speed. The flexibility in data speed offered by Bluetooth 5 allows low-power products to send more sophisticated data to the end user.
All Bluetooth versions are compatible and can work with the Bluetooth protocol.
For a better idea of how Bluetooth versions stack up, refer to the table below:
speed
Range
compatibility
power requirements
Reliability
Bluetooth Comparison
| Factors | Bluetooth 1 | Bluetooth 2 | Bluetooth 3 | Bluetooth 4 | Bluetooth 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | 732.2 kb/s to 1 Mbps | 2.1 Mbps | 24 Mbps (via Wi-Fi) | 1 Mbps (LE) | 2 Mbps (LE) |
| Range | 10 meters (33 feet) | 30 meters (100 feet) | 30 meters (100 feet) | 60 meters (200 feet) | 240 meters (800 feet) |
| Compatibility | N/A | OK for any phone | OK for any phone | It is good for any phone, but best for models with the same Bluetooth version | Good for any phone, best for newer phone models |
| Power requirement | High | High | High | Mid-high | Low |
| Reliability | Low | Low | Low | Mid-high | High |
Different Types of Bluetooth Technology:
The following are the classifications of Bluetooth technology:
Bluetooth headsets
Stereo headset
In-car Bluetooth headset
Bluetooth-equipped printer
Bluetooth enables webcam
Bluetooth keyboard
Bluetooth GPS device
Advantages of Bluetooth Technology:
With Bluetooth technology, there is an economic solution for the short distance.
There is no setup file to install the Bluetooth; it has in-built software.
Generally, we can see Bluetooth in smartphones, music players, speakers, etc.
Global technology specifications are used in Bluetooth.
Conclusion
Bluetooth is a technology used to connect data between smartphones and other electronic devices. It is commonly used to connect data between mobile devices, laptops, computers, headphones, speakers, printers, mice, keyboards, etc.
Bluetooth technology makes it very easy to exchange information and very convenient for the user. It can provide an effective distance less connection, which helps you avoid using network cables.
Bluetooth usually finds a related device and starts exchanging information between them without the user's permission at all. Any type of data, such as images, videos, audio files, organizational data, etc., can be easily connected through Bluetooth.
The latest version of Bluetooth technology has improved key features and security so that users can feel more reliable and secure about data connections.
FAQ’S
1. What is a Bluetooth version?
Answer: The most modern Bluetooth versions offer faster data transfer rates. Bluetooth offers greater connection range and reliability and provides better security than previous Bluetooth versions.
2. What is the best Bluetooth version?
Answer: Bluetooth 5.3: Depending on the bandwidth required, this version offers lower cost of use, greater connection security, and always better quality.
3. Why is the Bluetooth version important?
Answer: While the Bluetooth version doesn't affect the sound quality, it does make a huge difference.
4. What is the fastest version of Bluetooth?
Answer: Because Bluetooth 5 has high speed and data transfer, it can power the next generation of wireless services. This opens up more possibilities for companies to create an accessible and interconnected Internet of Things. IoT devices will work well with Bluetooth 5 and use its features properly.
5. Can we update the Bluetooth version?
Answer: Bluetooth versions are installed by the manufacturer on Android devices. So, you cannot update it on your Android phone.